Scan to BIM entailing conversion of Point Cloud Scan data to 3D Revit BIM models, removes guesswork on as-built conditions. It helps surveyors and laser scanning companies, make precise building analysis through detailed information extraction. This ensures better project planning and reliable reconstruction.
info@truecadd.com
Scan to BIM: Ultimate Guide for Point Cloud to BIM Modeling
Reconstruction or renovation projects usually present surveyors and laser scanning companies with multiple challenges related to information availability and as-built representation. Typically, in these cases, structural elements are damaged or missing, concealed or hard-to-reach, and available design records do not match the actuals. In architectural heritage monuments, slightest mistakes could mean courting a public backlash.
Adopting Scan to BIM or Point Cloud to BIM eliminates the risks that surveyors often face, including incorrect spatial analysis, design risks, and lack of visualization. Scan to BIM allows surveyors to easily navigate around architectural and structural complexities, and hard-to-reach MEP equipment.
Point cloud scans correctly depict all structures, spatial layout of elements, and as-built conditions to enable detection and diagnosis of every issue. With 3D Revit models reconstructed from point cloud data, architects and surveyors can easily resolve design clashes to ensure the sanctity of earlier architecture and project needs. But converting laser scan data to 3D models has its own challenges regarding the use of technology. Using specialized point cloud scan to BIM services ensures accuracy, data compatibility, and compliance.
Table of Contents
- What is Scan to BIM?
- Addressing Scan to BIM Challenges for Surveyors and Laser Scanning Companies
- How Surveyors Benefit from Scan to BIM Services
- Applications of Scan to BIM across Building Phases
- Tips and Tricks for Accurate Scan to BIM Modeling
- What are the different kinds of software used for Point Cloud to BIM Modeling?
- Why is Revit the most preferred software to create Scan to BIM models?
- How do you Convert Point Cloud Data to Revit?
- Best Practices for Converting Point Cloud to BIM
- 3 Quality Check Phases for Ensuring Accurate Scan to BIM Models
- Structured Scan to BIM Workflows for As-built Automation
- Top Advantages of Outsourcing Scan to BIM Services for Surveying Firms
- Conclusion
What is Scan to BIM?
Scan to BIM is a process where laser scanning technology captures the exact dimensions and conditions of a physical structure, producing a point cloud with millions of data points. These point clouds are then transformed into precise and comprehensive 3D BIM models using software such as Revit. These digital models are invaluable for tasks like renovations, remodeling, and facilities management, providing a highly accurate representation of the existing structure.
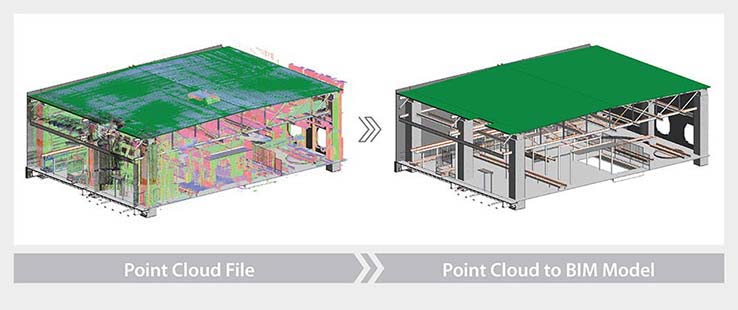 Point Cloud to BIM Model for a commercial building, Europe
Point Cloud to BIM Model for a commercial building, Europe
Addressing Scan to BIM Challenges for Surveyors and Laser Scanning Companies
Surveyors and laser scanning companies face numerous challenges due to the lack of drawings, records, and visibility of structural elements in existing buildings. Some common challenges faced by these professionals include:
- Inaccurate spatial analysis
- Unreliable cost estimates
- Absence of visualization
- Lower estimation accuracy
- Greater design risks
- Reduction in operational efficiencies
Don’t have the time to read the entire article right now?
That’s Ok. Let us send you a copy so you can read it whenever you want to. Tell us where to send it.
How Surveyors Benefit from Scan to BIM Services
Scan to BIM provides an effective solution to challenges posed by legacy surveying and reconstruction methods. It offers many high-impact advantages to surveyors and laser scanning companies.
Some advantages of Scan to BIM include:
Accurate spatial analysis
Spatial analysis is the key to evaluating interdependencies within various trades, including Architecture, Structure, and MEPF. An accurate, coordinated, and clash-free 3D model can support the division of building spaces and the extraction of each element in its space. An operational 3D model represents a processed version of the spatial model enhancing visualization.
Complete site mapping and precise spatial analysis with data-enriched 3D models validate design and constructability before construction begins.
Precise and reliable cost estimates
Laser scanners document every space and corner of a building’s architecture, structure, and MEPF system, leading to accurate and complete documentation of building structures. Using the 3D as-built BIM model, surveyors and cost estimators can calculate accurate cost estimates for each building component. They can leverage the as-built data in the 3D model to drive cost-efficient maintenance.
Presence of 360-degree visualization
Point Cloud to Revit BIM offers 360-degree visualizations through accurate, complete, and information-rich 3D models. Architects and surveyors can offer clients VR-ready walkthroughs of their 3D Point Cloud models to visualize every component in 3D space. Using 3D visualization helps surveyors in resolving errors early in a renovation or retrofit project. This promotes collaboration, informed decision-making, and quick turnaround.
Reduced design risks
Design errors pose a critical threat during renovation or remodelling. Heritage monuments hold great architectural significance. Artifacts, elements, or equipment within a heritage structure need to be preserved to emulate original conditions. Legacy processes and tools pose a high threat to renovating or remodelling complex heritage architecture, with MEP systems installed and working within the building.
In these cases, Point Cloud to BIM modelling for renovation and retrofit projects enhances design visibility and validity with data-rich 3D models. Knowing the placement or position of elements within the building reduces design risks or clashes. Parametric 3D modelling and generative design encourage accurate and efficient design prototypes to achieve the best possible design.
Improved operational efficiencies
Operational efficiencies of Scan to BIM include cost-effective ways to produce building products of high quality. Optimized production resources should reduce site waste, lower excess material consumption, mitigate product or service defects, and eliminate overproduction.
Plans and designs built on laser scanning data reduce the need for surveying personnel to visit the project site for multiple surveys. Capturing every detail in a 3D model built from a point cloud reduces field rework and downtime.
Lower health and safety hazards
Health and safety hazards during construction are a matter of serious concern within the construction industry. Using 2D plans offers little and imperfect visualization of spaces, dimensions, equipment, or materials. Working in hard-to-reach spaces to renovate high-rise structures or monuments can create safety issues when working with legacy tools.
Scan-to-BIM models offer a comprehensive representation of every space and corner for field personnel to view from a tablet-sized device. Equipment specifications, and annotations within a 3D model created with safety compliance standards, lower site safety risks.
Applications of Scan to BIM across Building Phases
Design Phase
A 3D BIM model helps architects and designers understand site conditions for accurate planning and informed decision-making in the design phase. The following parameters are crucial during the design phase for retrofit, renovation and restoration projects.
- Necessary building elements
- Necessary non-geometric attributes
- Necessary Level of Detail (LOD)
Scan to BIM helps preserve the architectural significance of heritage buildings or structures with accuracy, detailed coverage, space and angular resolution etc. during the design phase.
Construction Phase
During the construction phase, Scan-to-BIM models help identify ambiguities through the As-built model and the As-Designed 3D model. Tolerances within the 3D model are checked with standard regulations and codes for higher data accuracy and improved construction.
- Virtual field installation: The use of Scan-to-BIM for simulating installation and assemblies in virtual space helps identify and resolve potential issues or ambiguities before onsite construction commences. The efficient resolution of clashes at pre-construction stage saves rework and cost.
- Construction site safety: Plans and designs based on Scan-to-BIM workflow can greatly reduce site hazards and improve safety. Safety regulations and codes are mentioned within the 3D model for Architecture, Structure, and MEPF disciplines. These include International Code Council (ICC), State and Local Building Codes, International Green Construction Codes, International Fire Codes, etc.
- 3D reproduction: 3D model conversion from Point Cloud data such as drawings, photos, laser scans, or other input files facilitates quick design changes and visualization.
- Quality control: The Scan-to-BIM model is fabrication and installation ready and processed for Quality Assurance and Quality Control.
Facilities Management and Renovation
- Performance analysis: Point Cloud to BIM models are used for accessibility diagnosis, performance, and structural analysis. A performance analysis ensures optimum performance for energy consumption, structural validity, and accessibility.
- Accurate and complete documentation: Construction projects with inaccurate and incomplete documentation create problems for facilities managers and owners during maintenance and management. Scan to BIM generates an accurate, complete, and data-rich documentation set that can be used for maintenance and management. This documentation includes geometry, component names, specifications, warranty dates, and other parameters in a COBie format.
- Facilities management and renovation: 3D visualization enriched by data in 3D space ensures seamless FM functionality. Clients can realize operations and space management, renovation planning, emergency protocols, and other functionalities with the FM profile.

Don’t have the time to check the infographics right now?
That’s Ok. Let us send you a copy so you can check it whenever you want to. Tell us where to send it.
Tips and Tricks for Accurate Scan to BIM Modeling
Scan-to-BIM Modeling is a powerful tool to support a wide range of applications, including renovation, remodeling, and facility management of buildings. But it needs to be done accurately to achieve the required results and deliverables.
Interpreting the Point Cloud Data
Defining the point cloud file format with the right set of coordinates
- Review the point cloud scan data to resolve coordination issues
- Insert coordinates equivalent to the scan with a new point cloud position
- Set the base point based on shared coordinates
- Move the base point around the project coordinates to continue working in the original coordinate system
- Required graphical behaviours and precise Point Cloud displays can be achieved with coordinate accuracy
Align the point cloud to achieve improved mapping and consistency
- Collect multiple points to integrate scans
- Check the orientation of the scans in the local coordinate system
- Alignment and registration issues can be reduced by complementing the standard and scanned point cloud
- Extrapolate each point to retain density and direction to achieve rotational alignment
- Perform horizontal and vertical alignment after the rotational alignment is complete
Remove unwanted data from the scans to enhance scan-to-BIM performance
- Clean the noise of unwanted data from laser scans to reveal the required scan data or area
- Denoising the Point Cloud in the Recap and performing a Revit Export can help preserve the required features of the scans
- Accurate surface optimization can be achieved, and surface degradation can be removed through denoising
Compare scanned datasets with 2D plans and photos to enhance consistency, reduce RFIs, and lower rework
- Use 2D plans or 360-degree photos for comparison with the scanned dataset
- Comparison of 2D plans and 3D Point Cloud to BIM models with scan data can be used to create elevation views in the As-Built Cloud
- Integrated model concept removes errors, reduces budget and time overruns, and enhances model manipulation
Reduce large point cloud size to speed-up model processing
- Denoise the scans to remove unwanted data before running an import into Revit
- Place point cloud groups on worksets to improve file handling, visibility, and graphical override
- Break datasets into clusters and keep a copy to manipulate scanned file
- Setup a control model to define grids, coordinates, and levels for real-time modifications
Resolve building orientation to improve model accuracy and lower project duration
- Resolve orientation problems by setting accurate location based on Google Maps and True North
- Identify topographic elements through Google Earth for review and identification
- Create and identify component libraries for windows, doors, etc. to improve 3D model consistency
What are the different kinds of software used for Point Cloud to BIM Modeling?
Some popular and industry-recognized software used for Point Cloud to BIM are:
- Autodesk Revit®
- Navisworks®
- Autodesk Recap®
- Autodesk AutoCAD®
- Geomensura
Why is Revit the most preferred software to create Scan to BIM models?
Autodesk Revit is one of the most preferred tools in the AEC industry for creating scan to BIM models. It can be attributed to the various features of Revit, such as:
- Improved visualization: 360-degree visualization allows modelers to get exact information about building elements from scan data for creating BIM models.
- Multiple prototypes: Architects can directly use the model created using Revit as a base model to plan for alteration and renovation activities.
- Analysis and simulation: The Revit model can be used for further analysis and simulations of other aspects, such as energy consumption or accessibility. It can also produce 2D construction drawings and 4D construction deliverables, among others.
- Better collaboration: Revit collaboration tools help team members work in a collaborative shared model. This reduces clashes and improves coordination between stakeholders and various building disciplines.
- Precise dimensions and documentation: The scan to BIM model made using Revit is bi-directional. Even the tiniest edit anywhere in the model triggers automatic updates of every related component dimension and documentation.
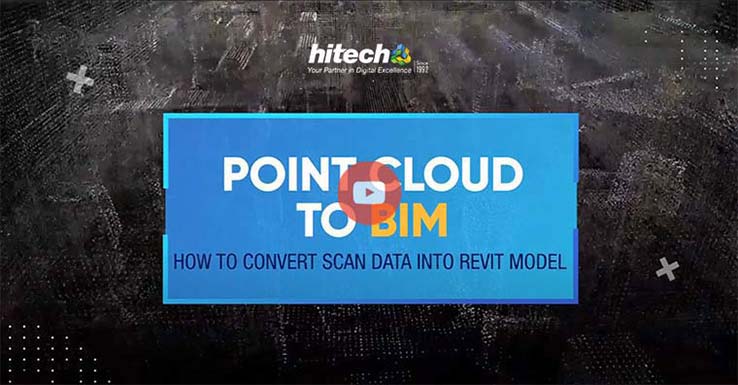
How do you convert Point Cloud Data to Revit 3D models?
Point cloud data can be converted to 3D models in Revit using a sequential step by step process. Check out the video to see how to convert point cloud data to a 3D BIM Revit model.
Best Practices for Converting Point cloud Scan to BIM
Here are a few tips for improving model accuracy, enhance project visualization, gain better mapping, and reduce project time.
- Use a rational coordinate system with a base point
- Ensure precise point cloud alignment or registration
- Remove unwanted data from the scanned data
- Always compare the scanned datasets with images, pictures, or drawings
- Avoid the use of large point cloud datasets
- Check resolution of building orientation
3 Quality Check Phases for Ensuring Accurate Scan to BIM Models
Step 1
- Understanding and identification of the required BIM application to gather and analyze information. This includes the required components to be modeled, specific Level of Development (LOD), and non-geometric attributes.
- After the BIM has been built from the scanned data, it is sent for approval through a quality check.
- The quality check identifies all the required scan information and attributes are included, LOD levels are met, and all the elements are modeled to specification.
Step 2
- BIM modelers analyze various building elements in the scanned data to model accurate Scan-to-BIM deliverables.
- Recognizing and categorizing various components such as floors, walls, ceilings, etc. helps generate an accurate and clean Scan-to-BIM model.
- Various building and component geometry are checked as per BIM model requirements.
- The placement and location of building elements based on actual scans and geometry are checked and matched for greater Scan-to-BIM accuracy.
Step 3
- Dimensional accuracies based on tolerances of building components built to regulations and codes play are checked for “As-Is” BIM quality.
- Tolerance deviation is checked and minimized. For example, if dimensional tolerances are set to 10mm, it is ensured that the scanned data does not allow over 10mm tolerance deviation in a modeled element.
- If elements cannot be modeled in the required tolerances, then a non-graphical mention needs to be included for clarity and further decision making.
Structured Scan to BIM Workflows for As-built Automation
As the construction industry experiences digital transformation, embracing new tools, approaches, and data-centric workflows ensures smooth and improved project outcomes. Digital workflows and technology used for point cloud geometry extraction can enhance productivity, eliminate risks, and cut costs.
The road to complete digitization for as-built automation is a connected approach through multiple technology sequences. The information generated from recorded data is used to automate Scan to BIM projects and allow stakeholders to perform jobs efficiently and quickly. The following infographic demonstrates how Scan to BIM workflow can be optimized from initial scanning to a digital inventory of as-built deliverables.
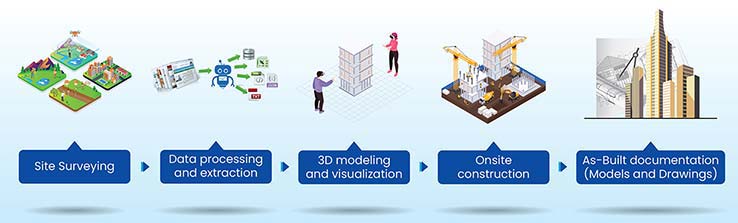
Top Advantages of Outsourcing Scan to BIM Services for Surveying Firms
Surveying firms can unlock significant advantages by outsourcing their Scan-to-BIM needs, such as:
- Assured and reliable quality of renovation design and construction.
- Faster planning processes and low project risks.
- Minimal errors in quick decision-making and project modifications.
- Higher project sustainability.
- Greater long-term cost savings.
- Quick communication, clarity, and collaboration in a Common Data Environment (CDE).
Conclusion
Scan to BIM will extend its horizon through the integration of various processes and tools. It is changing the way contractors, surveyors, architects, and other professionals, approach design, construction, and renovation. Connecting processes, people, data, and tools, Point Cloud to BIM will transform existing workflows to eliminate higher costs, and lengthy schedules, and deliver quality. AI and ML will continue to enrich the point cloud scan to BIM process by identifying scanned datasets to create high-performance 3D models.
Need help on an ongoing basis?
We establish long term business relationships with clients and are committed to total customer satisfaction.