Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) are fundamental systems of buildings that support required comfort and indoor quality. Knowing the fundamentals of HVAC helps to make informed decisions, ensure required energy performance, and perform maintenance and upgrades.
info@truecadd.com
HVAC Systems: Your Guide to Understanding Types, Functions, Components and More
Table of Contents
Effective design, fabrication, and installation of HVAC systems control air quality, humidity, and temperature for ensuring energy efficiency and optimal occupant comfort. However, accurate sizing, selection of HVAC equipment, breakdowns, longevity and maintenance are issues that often create challenges for stakeholders.
BIM-based MEP 3D modeling services offer effective solutions to overcome these hurdles. By enhancing coordination, ensuring design accuracy, improving fabrication precision, and streamlining installation, BIM helps deliver high-quality HVAC systems that meet performance standards and project timelines. Implementing BIM in HVAC projects not only overcomes challenges but also paves the way for improved efficiency and innovation in future HVAC projects.
In this article, we discuss the basics of HVAC systems. We also talk about the challenges with designing, fabrication and installation of HVAC systems, the types and functions of HVAC systems, the benefits of using BIM for HVAC layouts and the future trends in HVAC technology.

Brief overview of HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning)
HVAC equipment elevates the indoor environment with thermal equilibrium, humidity control, and air purity. Interconnected systems from compressors to heat exchanges and ductwork to thermostats can help manipulate fluid and thermodynamics to achieve optimal human welfare.
The function of HVAC systems extends beyond comfort, including air filtration for pollutant removal, humidity management to manage mold growth, and ventilation for adequate oxygen supply. A well-planned and designed HVAC system provides occupants with greater productivity, easier breathing, and rest within the built environment.
Streamline your MEP workflows with our MEP BIM services.
Outsource your MEP modeling projects now »Importance of HVAC in various environments
HVAC plays a vital role in diverse sectors, contributing to occupant comfort, safety, productivity, and overall well-being.
In residential and commercial buildings, they regulate temperature, humidity, and air quality for occupant comfort, health, and productivity. Industrial HVAC systems are often customized to protect equipment and materials, ensuring safe and efficient operations.
In healthcare, HVAC is crucial for infection control, maintaining sterile environments, and protecting patient health. Educational institutions rely on HVAC for comfortable learning, while the hospitality and transportation sectors use it to enhance customer experience.
Main functions of an HVAC system
Temperature control
HVAC systems maintain the required temperature based on cooling and heating. Heating components or furnaces raise temperatures in colder settings, while cooling coils and refrigerants lower temperatures in warmer settings. Consistent comfort is achieved by regulation of the heating and cooling process facilitated by thermostats.
Air quality
HVAC equipment helps filter and purify indoor air. Filters are used to trap allergens, dust, and pollutants, while some HVAC components utilize ionization and UV lights to neutralize harmful particles. The entire process enhances occupant health.
Humidity control
These systems control humidity levels based on humidification and dehumidification. Excess moisture is removed from the space with dehumidification, while humidifiers are used to enrich the dry seasons with greater moisture.
Air movement
HVAC equipment promotes air circulation using blowers, fans, and ductwork. Conditioned air is distributed evenly to remove stagnant air, manage consistent temperature, and improve overall comfort.
Coordinated and clash-free HVAC models led to cost savings for a hospital project in Ireland
An engineering contracting company contacted the team at TrueCADD for a hospital project in Ireland. With markup drawings and 2D basic drawings provided as input, the team at TrueCADD built coordinated and clash-free HVAC, plumbing, and fire protection models using Revit with precise shop drawings.
Results:
- Deliverables with 98% FTR
- Significant cost savings
 3D Revit MEP Coordinated Model for Plant Room
3D Revit MEP Coordinated Model for Plant Room
 3D MEP Model for Plant Room
3D MEP Model for Plant Room
How does HVAC work?
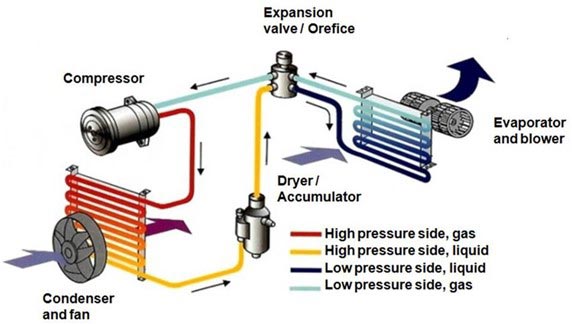 Source:Research Gate
Source:Research Gate
Heating
Furnaces
Gas furnaces are a common heating system that quickly warm homes by burning fuel to heat air. They are affordable and widely available, making them an attractive option for many homeowners, particularly in areas with colder climates. However, they require a gas line connection and pose a carbon monoxide risk if not properly installed and maintained.
Electric furnaces offer a cleaner alternative as they heat air directly without burning fuel. While safer and often cheaper to install upfront, they can be more expensive to operate and may struggle in extremely cold weather. On the other hand, oil furnaces are suitable where natural gas isn’t available and perform well in colder climates. However, they require fuel storage, more maintenance, and have a larger carbon footprint due to burning oil.
Boilers
- Steam Boilers: Ideal for large buildings, steam boilers provide even heat and humidification. They function by circulating pressurized steam through pipes. However, they require skilled operation, have high initial costs, and respond slowly to temperature changes. Safety risks associated with pressure and leaks are also a concern.
- Hot Water Boilers: Efficient for home heating, hot water boilers circulate hot water through pipes to radiators or under floor heating. They are safer and more responsive than steam boilers, with lower installation costs. However, they may be less efficient for larger spaces, require a pump, and do not humidify the air. Regular maintenance is necessary to prevent corrosion.
Ventilation
Ventilation involves the process of exchanging indoor air with outdoor air. Its purpose includes maintaining a comfortable and healthy indoor environment. The presence of fresh air renews oxygen levels, removes pollutants, and controls humidity, while exhaust equipment flushes out stale air and contaminants for required air circulation and prevents the buildup of harmful particles.
Energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) and heat recovery ventilators (HRVs)
| Features | Energy Recovery Ventilators | Heat Recovery Ventilators |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Differences | Energy Recovery Ventilators Transfers latest and sensible heat between incoming and outgoing airstreams. | Heat Recovery Ventilators Transfers sensible heat between incoming and outgoing systems. |
| Applications |
Energy Recovery Ventilators
|
Heat Recovery Ventilators
|
| Additional points |
AutoCAD
|
Heat Recovery Ventilators
|
Ventilation fans
Ventilation fans are critical to maintaining consistent air flow and quality in buildings. Supply fans are used to infuse fresh outdoor air, while exhaust fans remove contaminated air from the inside. Common types of axial fans include centrifugal fans and propeller fans.
Airflow requirements may fluctuate depending on the size of the space, occupancy, and use. Noise considerations are important in residential or quieter environments where silent fan models or noise canceling measures are needed.
Air conditioning
HVAC systems utilize various types of AC units to dehumidify and cool indoor spaces. These include –
- Split air conditioners
- Window air conditioners
- Ductless Mini-Split air conditioners
- Central air conditioners
- Packaged air conditioners
- Variable Refrigerant Flow/Volume (VRF/VRV)
Refrigeration cycle
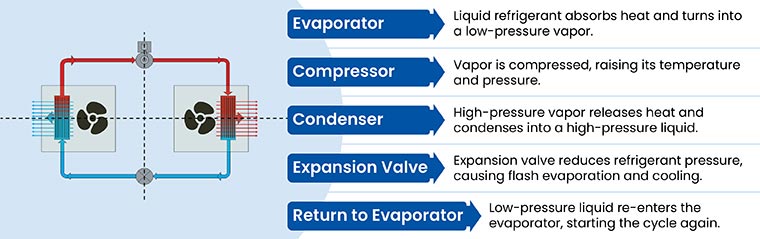
Types of HVAC systems
Centralized systems
Centralized HVAC systems use a central plant to condition air or water, distributing it throughout large buildings via ducts or pipes. This unified approach provides consistent climate control and simplifies maintenance.
Additionally, high upfront infrastructure costs and limited adaptability to layout changes are potential drawbacks. Despite these challenges, centralized systems remain popular for their efficiency and ease of maintenance in large-scale applications.
Decentralized systems (Ductless)
Mini-split systems are ductless HVAC options offering efficient zoned heating and cooling. With outdoor compressors and indoor air handlers, they eliminate ductwork and allow customized temperature control for each zone.
Window/wall units are affordable and easy-to-install solutions for smaller spaces. These self-contained units fit into windows or walls, but their limited capacity makes them unsuitable for larger areas. They can also be noisy and lack precise temperature control.
Hybrid systems
Hybrid HVAC units offer capabilities of both centralized and decentralized technologies for greater efficiency. A common configuration combines a heat pump and a furnace.
The heat pump is operated at moderate temperatures to provide effective cooling and heating. Significant drops in temperature activate the furnace to create warmth. This improves energy efficiency and provides comfort for building occupants.
Enhance your HVAC system’s efficiency with our expert MEP BIM services.
Contact us NOW »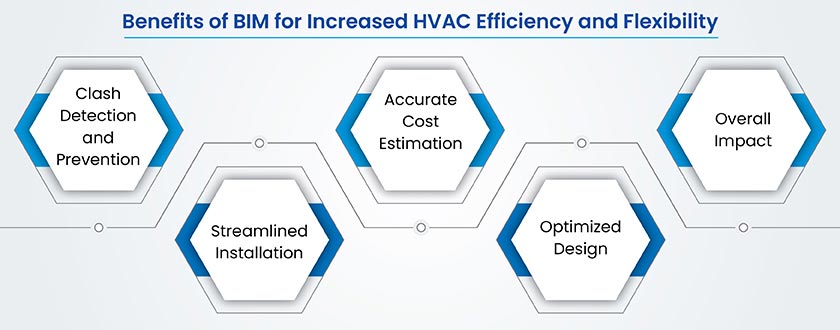
Energy efficiency and sustainability in HVAC
SEER – Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio
Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) is used to evaluate the energy efficiency of AC units. It displays the cooling output over a season divided by the total energy consumption. A high SEER value shows higher efficiency, leading to a reduction in energy consumption and a significant reduction in utility bills. A SEER rating of 14 or higher would provide greater energy savings and environmental impact.
AFUE – Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency
Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency or AFUE displays boiler or furnace heating efficiency. It also indicates that fuel energy converted to usable heat for 365 days. A greater AFUE rating fosters higher efficiency, lower energy waste, and a reduction in operating costs. Selecting a boiler or furnace requires model prioritization with AFUE ratings of 90% or higher to achieve energy savings and a reduction in carbon footprint.
HSPF – Heating Seasonal Performance Factor
Heating Seasonal Performance Factor or HSPF quantifies the heating efficiency of heating pumps. It is calculated over a period of one year. It determines the total heat output in British Thermal Units (BTU’s) divided by total electricity that is consumed in watt-hours. A greater HSPF points to higher efficiency. Selecting a heat pump with greater HSPF reduces the consumption of energy and cost of heating.
Importance of proper HVAC system sizing and maintenance
Proper sizing and maintenance are crucial for HVAC systems. Here are some energy-saving tips involving programmable thermostats, regular maintenance, and proper insulation.
- Programmable Thermostats: Proper sizing and maintenance of HVAC systems are essential for optimal performance and energy efficiency. Undersized and or oversized HVAC systems lead to energy waste and lack temperature consistency.
- Regular Maintenance: Perpetual maintenance that includes changes in filters, coil cleansing, and regular inspections ensure seamless operations and breakdown prevention.
- Proper Insulation: Deploying strategies for energy savings like thermostat programming for automatic temperature adjustment and maintenance of correct insulation within ducts and walls ensures minimal energy loss and results in reduction of utility bills and mitigated carbon emissions.
Renewable energy integration
- Solar-Powered HVAC: Integrating renewable energy sources within HVAC equipment facilitates cost-effective and sustainable results. Solar-driven HVAC with solar panels generates electricity, powering systems, and lowering grid reliance. This lowers the carbon footprint and operating costs.
- Geothermal Heat Pumps: The use of geothermal heat pumps harnesses stable earth temperature to achieve cooling and heating, leading to greater effectiveness and environmental influence.
Future trends in HVAC technology
- Smart HVAC systems with AI and IoT integration: AI and IoT are transforming HVAC systems into intelligent networks with adaptive thermostats, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance. AI optimizes energy usage based on user preferences and occupancy, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
- Advanced energy management and optimization: Advanced energy management uses data analytics, real-time monitoring, and machine learning to optimize HVAC energy consumption. This approach reduces costs, improves sustainability, and minimizes downtime through predictive maintenance.
- Increased focus on indoor air quality (IAQ): Growing health concerns prioritize Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) in modern HVAC systems. Advanced filtration captures allergens and viruses, while purification technologies neutralize harmful microbes. Real-time monitoring allows for dynamic adjustments to maintain healthy indoor environments.
Conclusion
Analyzing intricate HVAC systems is required to design healthy, comfortable, and energy-efficient indoor environments. Using the fundamental principles of HVAC and integrating them with various technologies would draw sustainability and efficiency. Staying informed with best practices and the latest trends can ensure spaces or zones within buildings remain healthy and comfortable.
Whether you are an HVAC engineer, contractor, building manager, or homeowner, a detailed understanding of HVAC equipment would help you make informed decisions for occupants.
Maximize efficiency and accuracy of MEP component installation and fabrication in your projects.
Contact our MEP BIM experts NOW »Need help on an ongoing basis?
We establish long term business relationships with clients and are committed to total customer satisfaction.